Thanks to good nutrition and medical advances, Canadians are living longer than ever before. But will our savings last as long as we do?
Q3 2022 market update: Economic uncertainty continues
Soaring inflation and rising interest rates weighed heavily on financial markets worldwide in the third quarter of 2022. Read on for our view of the global economy and financial markets.

Highlights
- Many central banks continued raising interest rates to stem inflation
- Rising wages and a sharp increase in the cost of food led to higher inflation
- Lower oil prices and declining real estate values helped temper inflation
- Global markets continued to struggle
- Stocks declined amid the inflationary environment
- Bonds also declined as interest rates moved higher
- The negative impact of the Russia-Ukraine conflict broadened
- Supply-chain issues persisted as the conflict passed seven months
- Europe faced an energy crisis as Russian energy exports slowed
A mixed picture on inflation
Markets and economists once again focused on inflation. Prices continued to rise significantly for food and many other goods.
The U.S. Federal Reserve Board maintained an aggressive stance on fighting inflation. The Fed increased interest rates again to help cool consumer demand.
The need to contain inflation also compelled the Bank of Canada (BoC) to raise its rates. So did the European Central Bank and Bank of England.
Higher interest rates slowed the willingness of businesses and consumers to take on more debt. Prices of real estate started easing with rising interest rates.
How are major economies doing?
- The U.S. economy contracted by 0.6%.
- China’s economy contracted by 2.6%.
- Europe’s economy grew by 0.8%.
- Japan’s economy grew by 3.5%.
A challenging quarter for global financial markets
Global equity markets declined broadly over the third quarter of 2022.
- Equities in most markets posted negative returns.
Economic activity also faced challenges amid varying degrees of COVID-related restrictions in China and other regions.
- Bond prices generally declined as yields rose amid aggressive action on interest rates. Concerns about a recession surfaced during the quarter as yield curves in Canada and the U.S. inverted (shorter-term yields rose more rapidly in relation to longer-term yields).
- Oil prices were unstable and declined over the quarter. Indications of reduced oil production could not support prices as slowing economic activity put pressure on global demand for oil.
- The price of gold decreased over the quarter amid geopolitical and economic uncertainty.
How is the Russia-Ukraine conflict affecting markets?
Geopolitical uncertainty continued to afflict the world. The ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict caused an energy crisis in Europe. Countries shunned Russian energy. Germany, Europe’s largest economy, felt the greatest impact of lower energy supplies.
How is the Canadian economy doing?
- The performance of Canada’s economy basically mirrored that of much of the developed world.
- The BoC raised its benchmark overnight interest rate by 100 basis points to 2.50% in July, its largest increase since 1998. The central bank raised rates again by 75 basis points in September.
- Yields fluctuated as investors weighed elevated inflation and rising interest rates against expectations of slowing economic growth.
- Canadian equities declined over the quarter. They were impacted by weakness in the energy and real estate sectors. Both sectors hold significant weighting in the S&P/TSX Composite Index.
- Canadian bond prices were largely unchanged. The yield on the 10-year Government of Canada bond finished slightly lower.
- Canada’s gross domestic product (GDP) grew an annualized 3.3% in the second quarter of 2022. This was in part due to an increase in household spending. The increase held despite prices and interest rates.
- Growth in business inventories was another strong contributor to Canada’s higher GDP figures in the second quarter. Economic activity in general has begun to show signs of slowing down.
- Canada’s labour market also weakened. The Canadian economy lost almost 40,000 jobs in August. This decline helped push up Canada’s unemployment rate to 5.4%.
How is inflation affecting the economy?
Canada’s inflation rate of 7.0% in August was its lowest level since April 2022. Consumer prices tumbled by 0.3% on a monthly basis.
The following chart shows the evolution of Canada’s inflation rate in 2022. A recent easing in gas prices has provided Canadians with some relief at the pumps. Oil prices have moved lower in recent months as well.
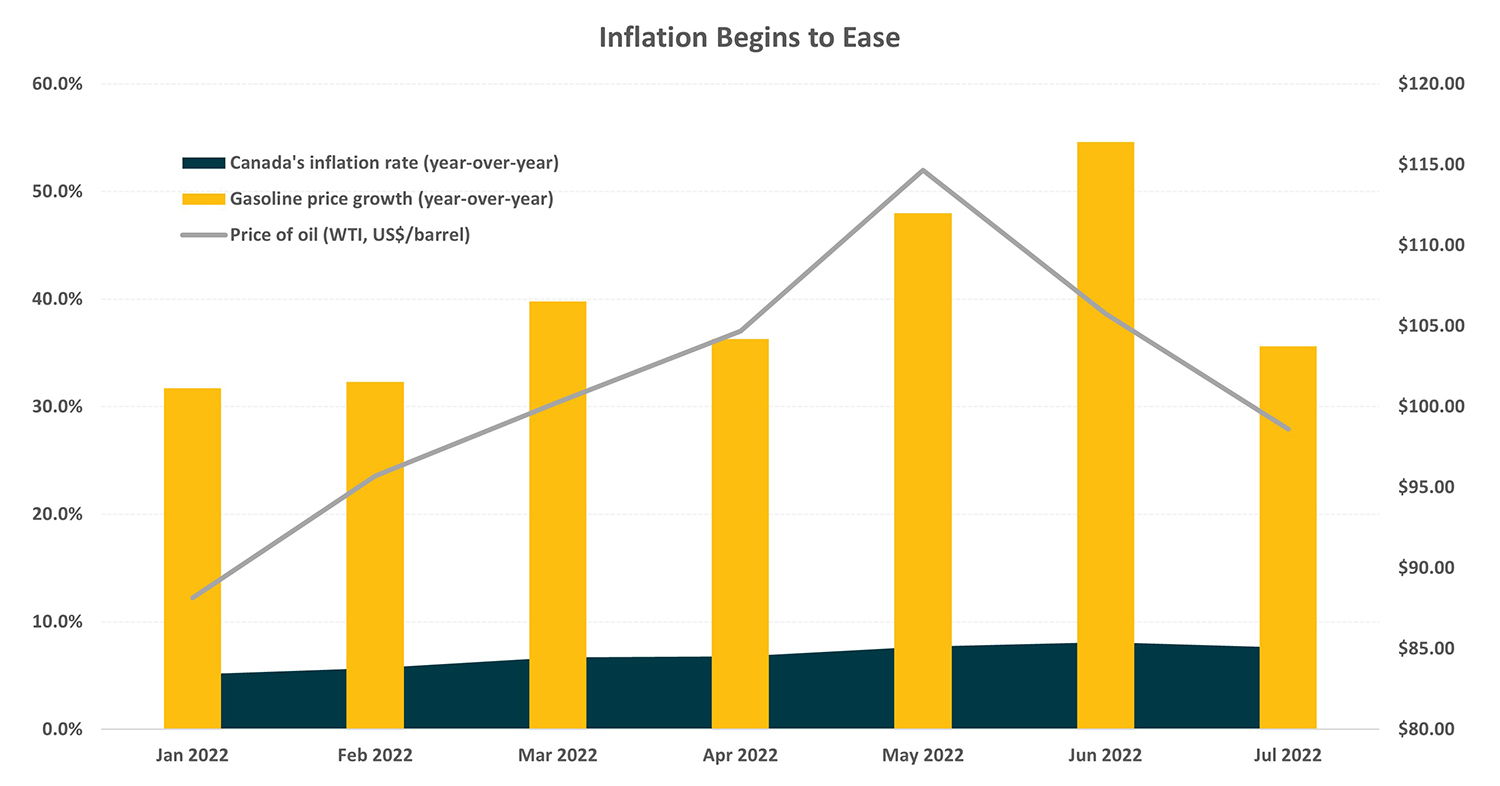
Source: Statistic Canada
What can investors expect in the future?
Factor |
Outlook |
|---|---|
Inflation |
Central banks are expected to continue raising interest rates to maintain their aggressive approach toward combatting inflation. |
Russia-Ukraine conflict |
The Russia-Ukraine conflict may continue to pose significant risk to the global economy. Europe is particularly vulnerable to inflationary pressures on energy products as supply dwindles. |
World economy |
Worldwide economic growth may slow amid tighter financial conditions and elevated price growth. These circumstances could push some economies into a recession. |
Canadian economy |
The Canadian economy may come under pressure as consumers face high prices and tightening financial conditions. Savings rates may decline as consumers’ purchasing power has been eroded by inflation and rising interest rates. |
Real estate |
The Canadian real estate market may cool further. Demand may weaken with high mortgage rates and persistently high home prices in some regions. |
Canadian interest rates |
The BoC noted that inflation has subsided but is still too high. Canada’s central bank is committed to bringing inflation back to its 2% target. The BoC is open to more interest rate increases to achieve this target. |
This commentary contains information in summary form for your convenience. Although this commentary has been prepared from sources believed to be reliable, Sun Life can’t guarantee its accuracy or completeness. Plus, this commentary is intended to provide general information and should not be seen as providing specific individual financial, investment, tax, or legal advice. The views expressed are those of the author and not necessarily the opinions of Sun Life. Please note, any future or forward-looking statements contained in this commentary are speculative in nature and cannot be relied upon. There is no guarantee that these events will occur or in the manner speculated.


